
Step 2: Kind is the subject of the sentence, so we need the nominative case. There are four cases in the German language: nominative, accusative, dative and genitive. Step 1: Child Kind, which is a neuter noun. In fact, the word Mdchen (girl) takes the neuter article das. Learn about German Nouns & German Articles German nouns have different articles - masculine, feminine and neuter. Right, let’s get stuck into the heart of the German language, the cases. We will explain what German cases are, give examples of each, and provide guidance to help you to identify which German case to use and when. With the indefinite article “ein“ it’s not clear whether the noun is masculine or neuter, for example “ein Taschenrechner“ (calculator) or “ein Handy“ (mobile phone). While that would make a ton of sense, the assignment of articles in German is much more random. Here, we will briefly introduce the German cases: the nominative case, the accusative case, the dative case, and the genitive case. The indefinite articles ein (masculine), eine (feminine), ein (neuter) correspond with ‘a/an’. The definite articles der (masculine), die (feminine), das (neuter), die (plural, all genders) correspond with “the“ in English. Nouns in German appear most of the time with an article, just like in English. It’s really good to learn the gender with the noun so you know whether it’s der, die or das or ein, eine or ein. Whereas words borrowed from English are usually neuter for example das Internet, das Baby. Words ending in e are usually feminine - die Lampe - ‘the lamp’. All German nouns are either masculine, feminine or neuter and, just as in English, they can be either singular or plural.
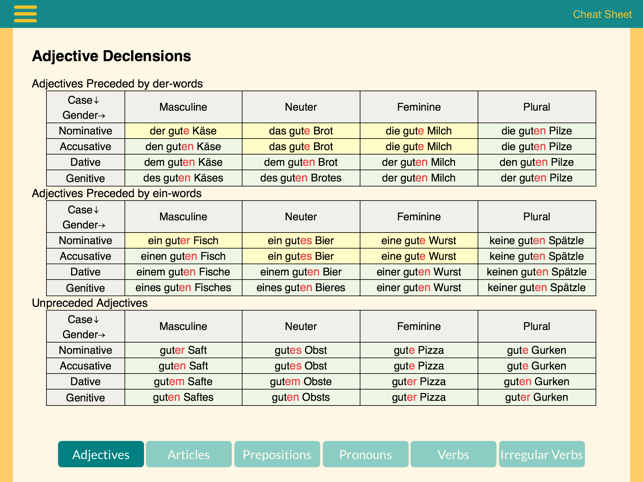

Our complete grammar explanations make learning German easy. In German, unlike English, the definite article the has many forms. These tips will help you get to grips with your German articles (der, die, das). The article DIE is also used to for the plural, irrespective of the singular gender, so. The German language is difficult to learn, especially German articles can be confusing. For example the days of the week are masculine - der Montag, and lots of drinks are also masculine too der Kaffee. Learn German grammar online with Lingolia. In German chair is masculine (DER Stuhl), book is neuter (DAS Buch) and apartment is feminine (DIE Wohnung). Sometimes there are groups of nouns that are a certain gender. Sometimes the gender is logical: ‘father’ is masculine - der Vater and ‘mother’ is feminine - die Mutter. What is an emphasizer in German Articles. German grammar has these indefinite articles: ein (masculine): Information: If the corresponding noun is in the plural, the indefinite article is omitted, as. So how do you know the gender of a noun? Well, there are clues to help you. Įine is ‘a’ for a feminine nouns - eine Katze and ein is ‘a’ for a neuter nouns - ein Kaninchen. So ein is ‘a’ for masculine nouns - ein Hund. įor masculine nouns der means ‘the’ - der Hund - ‘the dog’.įor feminine nouns die means ‘the’ - die Katze - ‘the cat’.Īnd for neuter nouns das means ‘the’ - das Kaninchen - the rabbit. These short articles precede nouns that can be people, places, or things. When you learn that the word for dog is Hund, learn that it’s a masculine noun - der Hund. So articles are words like a, an, and the.
#ARTICLES IN GERMAN GRAMMAR HOW TO#
How to use genders and articles in GermanĪll nouns in German are either masculine, feminine or neuter.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
